Modals of Ability! Learn how to use Modal Verbs to express ability in English with useful grammar rules, example sentences, video and ESL picture.
How to Use Modal Verbs To Express Ability
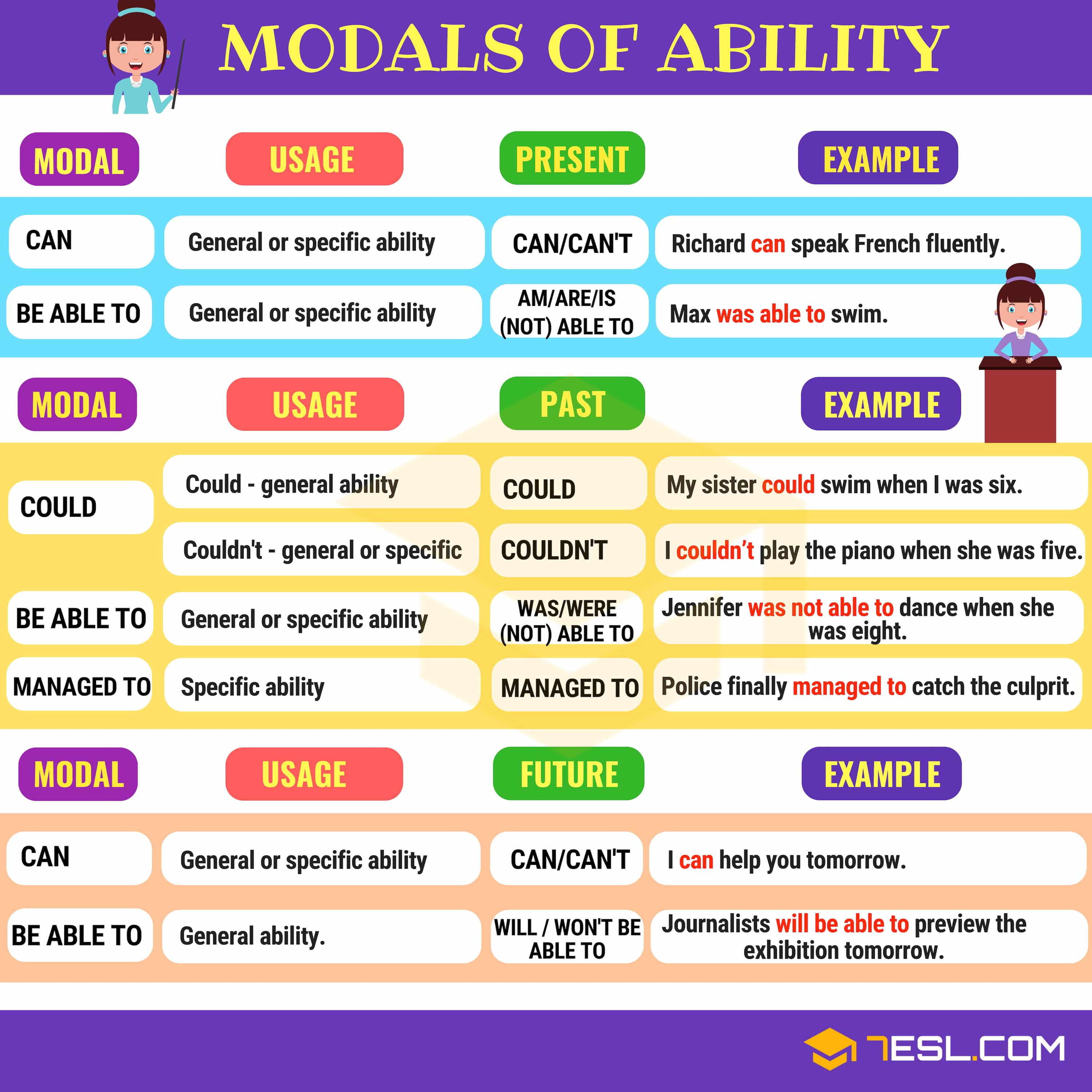
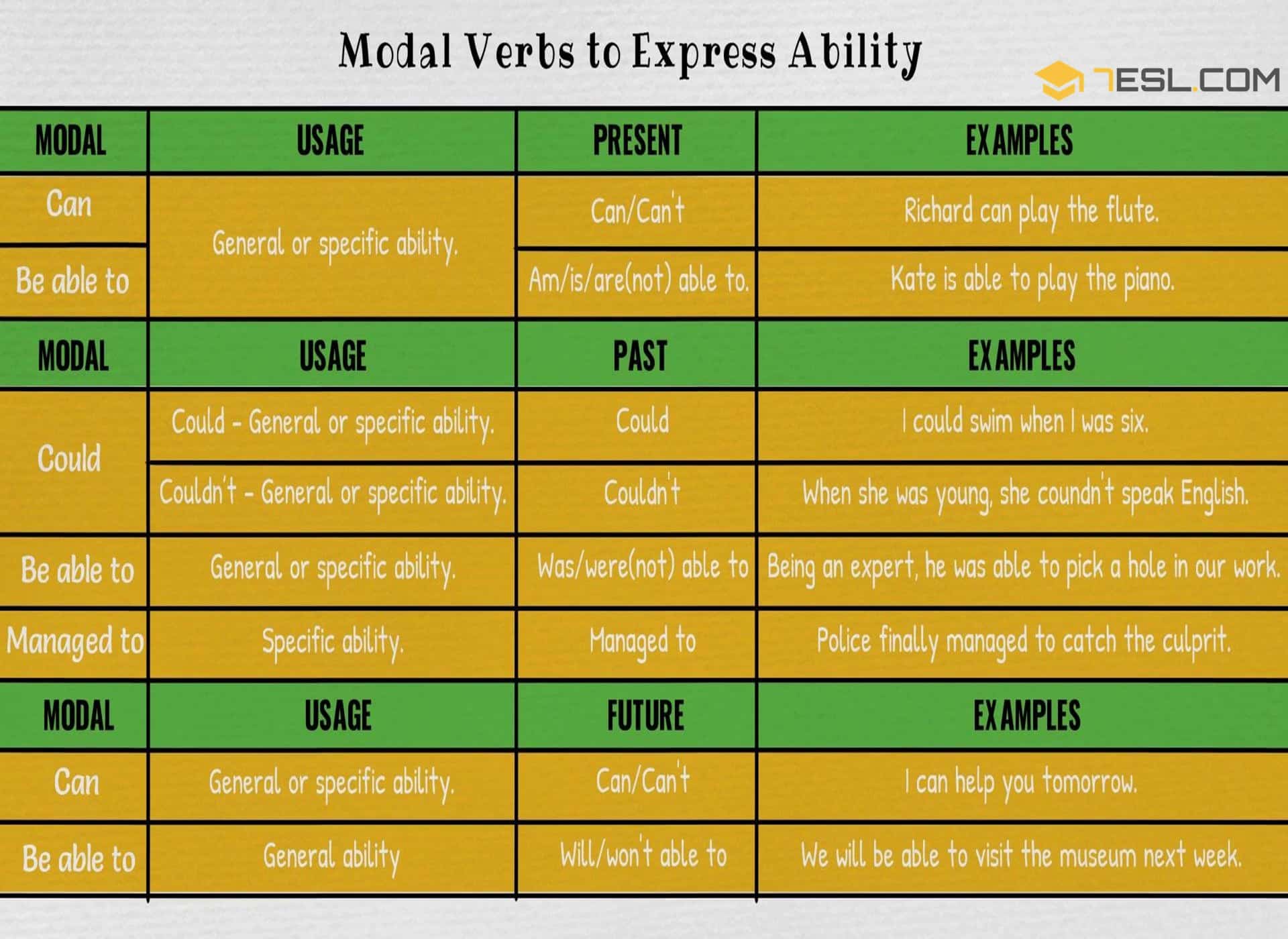
Ability can be expressed using modal verbs and phrases.
Present Forms | Modals of Ability
Be able to
- Form:
Is/am/are(not) able to + main verb
- Usage:
This form may be used in positive or negative, for general or specific ability.
- Modal verb examples:
James is able to cook steak.
David is not able to cook steak.
Can/Can’t
- Form:
Can/Can’t + main verb
- Usage:
This form may be used in positive or negative, for general or specific ability.
- Examples:
Richard can speak French fluently.
Gabriella can’t speak French fluently.
Past Forms | Modals of Ability
Be able to
- Form:
Was/were(not) able to + main verb
- Usage:
This form may be used, in positive or negative, for general or specific ability.
- Examples:
Max was able to swim fast when he was a young boy.
Jennifer was not able to dance when she was eight.
Could/Couldn’t
- Form:
Could/Couldn’t + verb
- Usage:
Could, in positive, is only used for general ability.
Couldn’t is used for general or specific.
- Examples:
I could swim when I was six.
My sister couldn’t play the piano when she was five.
Managed to
- Form:
Managed to + verb
- Usage:
This form is only used for specific ability: one time, one situation.
- Example:
Police finally managed to catch the culprit.
Future Forms | Modals of Ability
Be able to
- Form:
Will/won’t able to + main verb
- Usage:
This form is only used for general ability.
- Example:
Journalists will be able to preview the exhibition tomorrow.
Can/can’t
- Form:
Can/Can’t + verb
- Usage:
This form may be used, in positive or negative, for general or specific ability.
- Examples:
I can help you tomorrow.
I can’t come to her birthday party.
Modals of Ability | Image






0 Comments