Comparison of adjectives! Learn how to use comparative and superlative adjectives in English with example sentences and ESL printable worksheets.
In many languages, some adjectives are comparable. For example, a person may be “intelligent”, but another person may be “more intelligent”, and a third person may be the “most intelligent” of the three. The word “more” here modifies the adjective “intelligent” to indicate a comparison is being made, and “most” modifies the adjective to indicate an absolute comparison (a superlative).
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Three Forms of Comparison of Adjectives in English
Positive: it is an ordinary form of adjectives
Comparative: shows when two persons or objects being compared
Superlative: indicates that the quality or quantity is at its highest or is most intense
- Comparative are used to describe people and things.
– My car is fast but John’scar is faster.
– Emily is tall but Sophia is taller.
– I need a bigger car
- “Than” is used to compare one thing with another.
– Henry is older than Tom.
– Emily is smarter than Sophia.
– The second test was easier than the first one.
- “The” is used with a superlative:
– Where Are the Tallest Buildings in the World?
– Harry is the tallest student in this class.
- “As…as” is used to compare the attributes of two things that are equal
– Emily is as tall as Sophia.
– The first test is as easy as the second one.
General Rules in Forming Comparison of Adjectives
There are basic rules in forming the degrees of comparison:
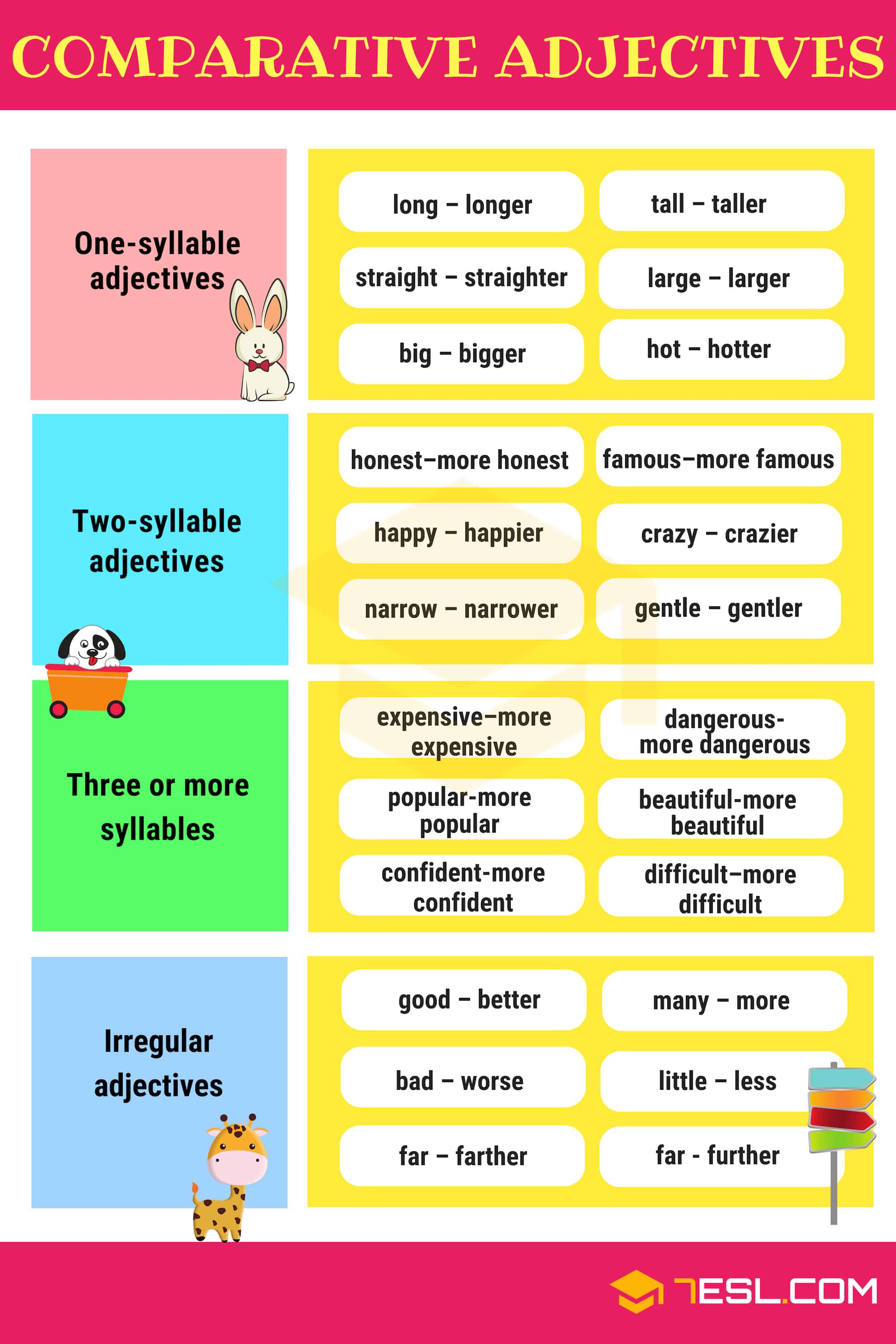
- For one-syllable adjective, add –er to form comparative and –est for superlative.
Examples:
- clear / clearer / clearest,
- dark / darker / darkest
- For most two-syllable adjectives, add –er for comparative and – est for superlative.
Examples:
- simple / simpler / simplest,
- gentle / gentler / gentlest
- For three or more syllables, always use more and most to form the comparative and superlative.
Examples:
- creative / more creative / most creative
- Some adjectives end with a consonant letter y, change y to I and add –er or -est.
Examples:
- busy / busier / busiest,
- merry / merrier / merriest
- Some adjectives end with a single vowel and single final consonant letter. Double the final consonant and add –er/-est.
Examples:
- thin / thinner / thinnest,
- fat / fatter / fattest
- When the adjectives end in “e”, add –r for the comparative and –st for superlative
Examples:
- wise / wiser / wisest,
- simple / simpler / simplest
- Irregular comparisons of adjectives are compared irregularly
Examples:
- good / better / best
- ill / worse / worst
Comparison of Adjectives: Forming Comparatives
Comparison of Adjectives: Forming Superlatives
Comparison of Adjectives: Forming Equative, Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Notes for Irregular Comparison of Adjectives
(Exceptions)
Irregular Comparisons:
- Far / Farther than / the Farthest
- Far / Further than / the Furthest
Farther and Farthest generally refer to distance
Further and Furthest also refer to distance but they may have the meaning of “additional”
“His voice carried farther than mine.”
“Further analysis of the data is needed.”
- Old / Older than / the Oldest
- Old / Elder than / the Eldest
Older and Oldest refer to persons or things;
Elder and Eldest can only be used for members of the same family
“My elder sister is a doctor.”
“The older generation doesn’t like pop music.”
but Elder cannot be placed before Than so Older is used:
“Henry is my elder brother; he is two years older than I.”













0 Comments